Science
How Many Questions Are on the CISA Exam? Explained for Aspiring Candidates

Introduction to CISA Exam
The Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) exam is a crucial step for individuals seeking a career in information systems auditing, control, and security. It’s administered by ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) and is highly respected in the IT industry. Understanding the exam structure, including the number of questions, is vital for aspirants aiming to excel in this field.
CISA Exam Overview
The CISA exam evaluates a candidate’s knowledge and proficiency in information systems auditing, control, assurance, and security. It consists of multiple-choice questions designed to assess various domains related to auditing, such as information systems, governance, risk management, and more.
Understanding the Question Format
The exam comprises multiple-choice questions with four answer options. Candidates need to select the most appropriate answer from these choices. The questions are structured to test not just knowledge but also the application of concepts and scenarios that auditors commonly encounter.
Question Types in the CISA Exam
The CISA exam primarily presents multiple-choice questions to candidates. These questions consist of a stem, which poses a query or presents a scenario, followed by four answer choices. Candidates are required to analyze the information provided and select the most appropriate response among the options given.
Scenario-Based Questions
A significant portion of the CISA exam includes scenario-based questions. These questions present real-world situations that information systems auditors might encounter in their professional roles. Candidates need to apply their knowledge and expertise to identify the best course of action or solution within the given scenario.
Emphasis on Application and Analysis
The exam questions not only test theoretical knowledge but also the ability to apply concepts in practical contexts. Candidates are expected to demonstrate their analytical skills by evaluating scenarios, understanding the implications of different actions, and choosing the most suitable responses.
Time Management in Answering Questions
Efficient time management is crucial during the exam. Candidates should aim to understand the questions swiftly, analyze the presented information, and select the most appropriate answers without spending excessive time on any single question. This ensures that all questions are adequately addressed within the allocated exam duration.
Preparation Strategies for Question Format
To excel in the CISA exam’s question format, candidates should practice answering different types of questions. Utilizing practice exams, mock tests, and sample questions can help familiarize candidates with the question structures and enhance their ability to select the most suitable responses within the given scenarios.
Understanding the question format is pivotal for candidates preparing for the CISA exam. Practicing various question types and honing analytical skills can significantly contribute to success in navigating the exam’s multiple-choice format and scenario-based queries.
How Many Questions are on the CISA Exam?
The CISA exam consists of 150 multiple-choice questions. These questions cover five domains:
- Domain 1: Information System Auditing Process (21%)
- Domain 2: Governance and Management of IT (16%)
- Domain 3: Information Systems Acquisition, Development, and Implementation (18%)
- Domain 4: Information Systems Operations and Business Resilience (20%)
- Domain 5: Protection of Information Assets (25%)
Each domain has a specific weightage, indicating the proportion of questions related to that domain in the overall exam.
Scoring and Passing Criteria
To pass the CISA exam, candidates need to achieve a scaled score of 450 or higher. The scores range from 200 to 800, with 450 being the minimum passing score. ISACA uses a scaling process to adjust the raw scores based on the difficulty level of the questions.
Tips for CISA Exam Preparation
- Familiarize yourself with the CISA exam content outline provided by ISACA.
- Utilize study materials and resources recommended by ISACA, such as official study guides and practice exams.
- Engage in hands-on practice and real-world scenarios to reinforce your understanding.
- Consider joining study groups or forums to discuss concepts and clarify doubts with peers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the CISA exam consists of 150 multiple-choice questions distributed across five domains. Aspiring candidates should thoroughly prepare for each domain, understand the question format, and utilize available study materials to increase their chances of passing the exam successfully.
Remember, success in the CISA exam not only requires knowledge but also the ability to apply concepts in real-world scenarios, making it essential for professionals in the field of information systems auditing and security.
By comprehending the structure and number of questions in the CISA exam, candidates can strategize their preparation effectively and work towards achieving their certification goals in the field of information systems auditing.
Science
Understanding Telomere Function: Guardians of Chromosomal Integrity
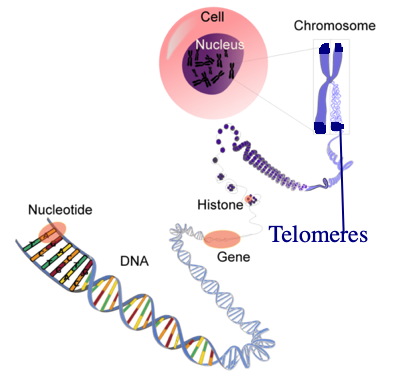
Introduction to Telomeres
Structure of Telomeres
Telomeres: Architectural Marvels at Chromosome Ends
1. Composition of Telomeres
Telomeres, intricate structures composed of repetitive DNA sequences, typically comprise tandem repeats of the sequence “TTAGGG” in vertebrates. This repetitive sequence forms the core of telomeric DNA, often spanning from a few hundred to several thousand base pairs. Additionally, telomeres boast a specialized configuration known as the T-loop, where the single-stranded overhang of the telomeric DNA loops back to interact with the double-stranded region, contributing to their stability and protection against degradation.
2. Shelterin Proteins and Their Role
Shelterin, a vital complex of proteins, binds intricately to telomeric DNA, safeguarding these terminal regions from degradation and preventing them from being identified as damaged DNA strands. Key components of the shelterin complex include TRF1, TRF2, and POT1, each playing distinct roles in maintaining telomeric integrity. TRF1 and TRF2, for instance, aid in forming and stabilizing the T-loop structure, while POT1 helps protect the single-stranded telomeric overhang, shielding it from being recognized as a DNA break and activating repair mechanisms.
Understanding the intricate composition and the protective role of shelterin proteins in maintaining the structure of telomeres provides insights into the mechanisms preserving chromosomal integrity and overall cellular health.
Telomerase: The Guardian Enzyme
Telomerase, a specialized ribonucleoprotein enzyme, is pivotal in maintaining telomere length. Comprising an RNA template and a catalytic protein component (reverse transcriptase), telomerase actively replenishes telomeric sequences, counteracting the natural shortening that occurs with each cellular division. This ability to elongate telomeres is particularly crucial in highly replicative cells, such as stem cells and germ cells.
Role in Cellular Senescence and Aging
As cells divide, telomeres progressively shorten due to the “end replication problem,” where DNA polymerase is unable to replicate the extreme ends of linear chromosomes. This gradual shortening serves as a molecular clock, eventually triggering cellular senescence or the cessation of cell division. This process is implicated in the aging of cells and, by extension, in the aging of organisms.
Telomeres: Key Players in Cellular Senescence and Aging
1. Telomere Shortening and Cellular Senescence
As cells undergo division, the natural process of DNA replication faces challenges at the ends of linear chromosomes, leading to the gradual shortening of telomeres. This phenomenon, known as the “end replication problem,” results in the erosion of telomeric DNA with each cell division. Eventually, as telomeres reach a critically short length, cells enter a state of replicative senescence, where they cease to divide further. This limitation on cellular division is a protective mechanism to prevent damaged or potentially unstable cells from proliferating, contributing to tissue aging and overall organismal aging.
2. Implications in Aging and Age-Related Diseases
Telomere shortening is intricately linked to the aging process. As cells reach their replicative limit and enter senescence due to critically shortened telomeres, tissues and organs experience reduced regenerative capacities and increased vulnerability to age-related diseases. Studies have associated shortened telomeres with various age-related conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and certain cancers. The role of telomeres in regulating cellular lifespan underscores their significance in understanding the mechanisms underlying aging and age-associated diseases.
Comprehending the relationship between telomere shortening, cellular senescence, and aging sheds light on potential therapeutic avenues aimed at preserving telomere length or mitigating the adverse effects of telomere attrition, thereby contributing to healthier aging and improved quality of life.
Implications in Disease and Health
Telomere dysfunction has been linked to various age-related diseases and conditions. Shortened telomeres have been associated with increased susceptibility to certain cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and other ailments. Conversely, maintaining optimal telomere length through healthy lifestyle choices, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management, may potentially contribute to overall well-being and longevity.
Telomeres and Cellular Reprogramming
Innovative research in cellular reprogramming has highlighted the significance of telomeres in reversing cellular aging. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), generated from adult cells, undergo telomere elongation during the reprogramming process, restoring their telomeric length and reversing the age-associated markers, providing promising avenues for regenerative medicine.
1. Telomeres in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
In the realm of cellular reprogramming, particularly the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), telomeres emerge as critical players. Throughout the process of reprogramming, where mature cells are transformed into a pluripotent state, the activity of telomerase—a key enzyme responsible for elongating telomeres—becomes pivotal. Studies have illuminated that during cellular reprogramming, iPSCs, derived from adult cells, experience telomere elongation. This rejuvenating process resets telomeres, effectively reversing age-related markers and restoring telomeric length to levels akin to embryonic stem cells.
2. Potential Applications in Regenerative Medicine
Delving into the role of telomeres in cellular reprogramming holds tremendous promise for regenerative medicine. The capacity to reset telomeres during the reprogramming of somatic cells into iPSCs not only revitalizes cellular characteristics but also offers an avenue for generating patient-specific cells for therapeutic purposes. This innovative approach presents exciting prospects for developing personalized regenerative therapies, circumventing immune rejection concerns, and potentially addressing a spectrum of degenerative diseases.
Unraveling the link between telomeres and cellular reprogramming not only unveils the mechanisms governing cellular rejuvenation but also heralds a new era in regenerative medicine. These insights hold the potential to revolutionize treatments by tailoring them to individual needs, offering hope in the quest to address various age-related conditions and advancing personalized medicine.
Telomeres: Pivotal in Cellular Reprogramming
1. Telomeres in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
Cellular reprogramming, particularly the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), involves the transformation of mature cells into a pluripotent state. During this process, the activity of telomerase, the enzyme responsible for elongating telomeres, becomes crucial. Studies have shown that iPSCs, derived from adult cells, undergo telomere elongation as part of the reprogramming process. This reprogramming-associated elongation resets the telomeres, reversing age-related markers and restoring telomeric length comparable to embryonic stem cells, thereby rejuvenating the cellular state.
2. Implications for Regenerative Medicine
Understanding the role of telomeres in cellular reprogramming holds immense promise for regenerative medicine. The ability to reset telomeres during the reprogramming of somatic cells into iPSCs not only rejuvenates the cells’ characteristics but also provides a potential avenue for generating patient-specific cells for therapeutic purposes. This avenue presents exciting prospects for developing personalized regenerative therapies, bypassing immune rejection issues and potentially treating various degenerative diseases.
Exploring the connection between telomeres and cellular reprogramming not only unveils the mechanisms behind rejuvenation at a cellular level but also opens doors to innovative approaches in regenerative medicine, paving the way for personalized treatments and addressing age-related ailments.
Conclusion
In summary, Telomere Function stand as guardians of genomic stability, preserving chromosomal integrity and influencing cellular lifespan. Understanding their function not only sheds light on fundamental aspects of cellular biology but also holds promising implications in the fields of aging, disease prevention, and regenerative medicine.
Remember, while the science of telomeres continues to unravel their mysteries, fostering healthy habits may contribute to maintaining optimal telomere length and potentially enhance overall health and longevity.
Health
Are Teeth Considered Bones? Exploring the Distinction

Introduction: Teeth vs. Bones
Teeth and Bones: A Comparative Analysis
Similarities in Structure and Composition
Function and Purpose
Bones serve multiple critical functions, including providing structural support, protecting organs, producing blood cells, and storing minerals. In contrast, teeth have a distinct purpose related to digestion and speech, although they are part of the skeletal system.
Composition and Anatomy
Teeth consist of enamel, dentin, pulp, and cementum. Each layer plays a crucial role in the tooth’s structure, sensitivity, and attachment to the jawbone. Understanding the anatomy of teeth reveals their unique nature compared to bones.
Developmental Differences:
Embryonic Origin
Teeth and bones have different origins during embryonic development. Teeth derive from the ectoderm, while bones originate from the mesoderm. This distinction contributes to their disparate structures and functionalities.
Developmental Processes
Nutrition and Maintenance of Teeth and Bones
Calcium and Vitality
Proper Nutrition for Dental and Bone Health
Conclusion: Appreciating the Unique Roles
Health
CVS Pharmacists Walkout: Understanding the Grievances and Impact
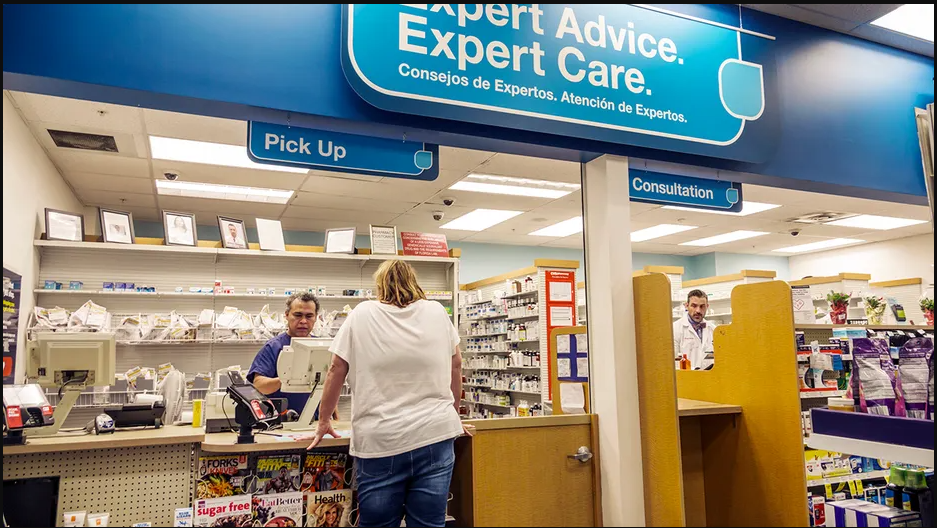

Introduction:
1. Overview of the CVS Pharmacists Walkout
In recent events, CVS pharmacists across several locations have initiated a walkout. Understanding the reasons and implications sheds light on this critical development.
- Triggering Factors: Increased workload and staffing inadequacies catalyzed the CVS pharmacists’ walkout, highlighting critical concerns impacting their working conditions.
- Scope and Locations: The CVS pharmacists’ walkout spans multiple locations, impacting various branches and regions, emphasizing the widespread nature of this movement.
2. Core Issues Driving the Walkout
- Workload and Staffing Concerns: The walkout stems from mounting workload pressures and inadequate staffing levels, jeopardizing patient safety and necessitating urgent improvements in working conditions and staffing support.
- Patient Safety and Health Care Standards: The walkout emphasizes concerns over compromised patient safety and declining healthcare standards, urging measures to uphold quality care and pharmacist well-being.
3. Impact on Pharmacist-Patient Dynamics
Delving into the impact of this walkout on the pharmacist-patient relationship and community health services offers a broader perspective.
- Service Disruption: The CVS walkout disrupts pharmacy services, impacting patient access to medications and highlighting the significance of pharmacist roles in healthcare.
- Community Health Impact: The walkout’s broader impact extends to community health services, underscoring the interconnectedness between pharmacist roles and the broader landscape of healthcare provision and access.
4. Responses from CVS and Pharmacists’ Advocacy
- Corporate Response: CVS’s official response involves statements and actions addressing the pharmacist walkout, aiming to mitigate disruptions and potentially resolve issues. This corporate reaction signals the importance of addressing pharmacist concerns while ensuring continued service and patient care.
- Advocacy Efforts: Pharmacist advocacy groups drive efforts to address concerns regarding workload, staffing, and patient safety. Their initiatives focus on pushing for improved working conditions and heightened healthcare standards, advocating for changes essential to both pharmacists’ well-being and patient care quality.
5. Public Opinion and Support
- Community Support: The CVS pharmacists’ walkout garners significant backing from communities, reflecting widespread support for their cause and concerns about healthcare standards and pharmacist well-being.
- Social Media Impact: Social media amplifies voices, rallying support for CVS pharmacists’ cause. Platforms showcase public sentiment, playing a pivotal role in galvanizing community backing and spotlighting concerns over healthcare standards and pharmacist working conditions.
6. Potential Resolutions and Future Implications
Looking towards potential resolutions and understanding the possible ramifications of this walkout on the future of pharmacist work environments and healthcare systems.
- Resolution Prospects: Exploring potential solutions to address pharmacist concerns and restore normalcy.
- Industry-Wide Impact: Assessing how this event might impact the broader landscape of pharmacist work conditions and healthcare practices.
Conclusion:
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoKooraLive English: Guide to Live Sports Streaming
-
 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoSSIS 816 Revolutionizing Data Integration
-
 Health7 months ago
Health7 months agoOptimizing Health: The Comprehensive Guide to TG Tubes
-

 Lifestyle6 months ago
Lifestyle6 months agothe Charm of Villages: Decoding the Loofa Code
-

 Entertainment6 months ago
Entertainment6 months agothe Mystery: packgod face reveal
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoSimplifying Work Life: NetchexOnline Employee Login
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoThe Power of Innocams
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoExploring the Marvels of Jable.tv: A Comprehensive Guide to Streaming Excellence